Yoga is more than just physical postures—it’s a holistic practice that nurtures the body, mind, and spirit. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced practitioner, understanding Yoga Anatomy is key to making the most of your practice. At Sage House Yoga, we believe that knowing how the body works can enhance your alignment, prevent injuries, and deepen your connection with your practice. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of yoga anatomy and why it’s essential for every practitioner.
What is Yoga Anatomy?
Yoga anatomy refers to understanding the human body’s structure and how it moves. It’s about knowing how muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, and the nervous system come together to facilitate the different poses in yoga. When you understand how your body functions during yoga, you can adjust your movements for better results and injury prevention.
Key Elements of Yoga Anatomy: A Deeper Understanding
Yoga anatomy is not just about learning the names of muscles and bones; it’s about understanding how the body functions as a whole system during each pose. A deep comprehension of anatomy helps you practice with precision, prevents injuries, and improves your performance on and off the mat. Let’s break down the key elements of yoga anatomy that every practitioner should understand.
1. Musculoskeletal System: The Foundation of Movement
The musculoskeletal system forms the foundation of yoga practice. It comprises bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage—all of which work together to enable movement and provide structure. A deeper understanding of the musculoskeletal system allows you to understand how different muscles engage during various poses and helps you align your body correctly.
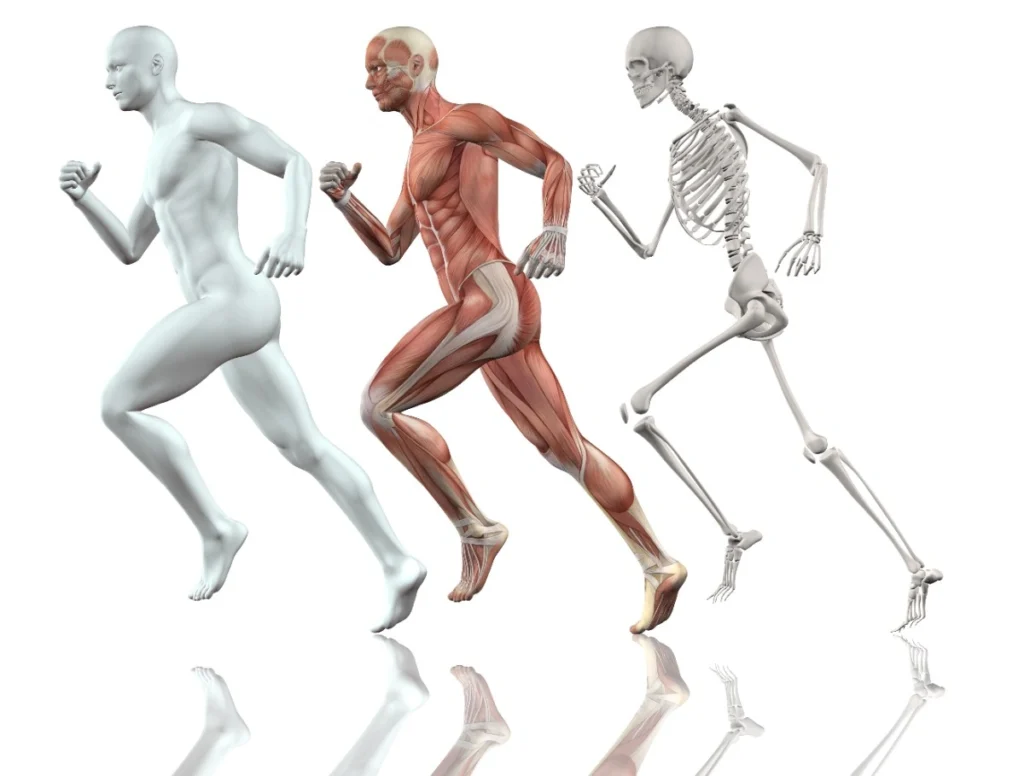

Bones: Your bones serve as the framework of your body. They give you structure and form and provide a base for muscle attachment. In yoga, understanding the alignment of bones, especially in the spine, pelvis, and limbs, is crucial for ensuring safe practice.
Muscles: Muscles are responsible for movement and providing stability to the body. In yoga, different postures require specific muscle engagement. For instance, in Warrior I (Virabhadrasana I), your quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves engage to stabilize your legs, while your shoulders and arms engage to extend through the fingertips.
Tendons and Ligaments: Tendons connect muscles to bones, and ligaments connect bones to other bones. Understanding these structures helps you avoid overstretching or overextending in poses, especially in areas like the hamstrings or lower back where tendons are particularly vulnerable.
At Sage House Yoga, we emphasize the importance of musculoskeletal alignment in our Yoga Teacher Training programs, helping students learn how to align the body in every asana to maximize benefits and minimize risk.
2. Nervous System: The Mind-Body Connection
The nervous system plays a key role in your yoga practice because it controls the communication between your brain and muscles. Understanding how this system operates helps you harness the power of mind-body connection, which is central to yoga.
- Central Nervous System (CNS): The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. It sends and receives signals from the body’s muscles and organs, helping you perform movements with precision. For example, when you engage in Pranayama (breathing exercises), your CNS helps regulate your breathing rate and depth, impacting your energy levels and calming the mind.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This network extends beyond the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body, including muscles and sensory organs. In yoga, activating the PNS through relaxation techniques such as Yoga Nidra or Savasana (Corpse Pose) helps reduce stress, improve sleep, and enhance mental clarity.
Understanding the nervous system allows you to practice mindfulness and cultivate a deeper awareness of your body and breath. At Sage House Yoga, Pranayama and meditation techniques are core parts of our Yoga Retreats and Teacher Training Programs, teaching you how to control your nervous system for better health and well-being.
3. Breathing Mechanism: The Heart of Pranayama
Breathing is one of the most vital functions of the body, and in yoga, Pranayama (breathing exercises) serves as the bridge between body and mind. Understanding the anatomy of breathing can greatly enhance your practice, making it more effective and conscious.
- Diaphragm: The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle located beneath the rib cage. It plays a critical role in breathing by expanding and contracting the lungs. In yoga, diaphragmatic breathing (using the diaphragm efficiently) helps increase lung capacity, improve oxygen flow, and promote relaxation.
- Intercostal Muscles: These muscles are located between your ribs and help expand the chest during breathing. Expanding the ribs laterally (side-to-side) is an important aspect of proper breathwork, especially in poses like Utkatasana (Chair Pose), where the chest needs to be open and lungs fully expanded.
- Abdominal Muscles: The abdominal muscles play a role in exhalation. Engaging them helps expel air more efficiently from the lungs. Breath control is a significant aspect of Pranayama, and understanding how to engage your core muscles during specific breathwork techniques enhances your practice.
At Sage House Yoga, you’ll learn various breathing techniques through our Yoga Teacher Training and Retreat Programs that focus on Pranayama and mindful breathing. These techniques help control the flow of energy (prana) within the body, leading to better health, focus, and inner peace.
4. Fascia and Connective Tissue: The Web of Support
Fascia is a form of connective tissue that surrounds muscles, bones, and organs, providing structural support and facilitating movement. Fascia is interconnected throughout the entire body, and its health and flexibility are integral to overall mobility.
- Myofascial Release: Understanding how fascia works is especially helpful for practices like Yin Yoga, which targets the fascia to release stored tension and increase joint mobility. This understanding helps practitioners use foam rolling or specific yoga poses to release tightness and improve flexibility.
- Collagen: Fascia is composed largely of collagen fibers. As you practice yoga, fascia lengthens and becomes more pliable, allowing for greater range of motion. Poses like Downward Dog and Forward Bends stretch the fascia along the spine and hamstrings, enhancing flexibility and muscle health.
Incorporating myofascial release and fascia-friendly poses is something we emphasize during our Yoga Retreats and Teacher Training programs at Sage House Yoga, which helps you maintain structural integrity and prevent injuries over time.
5. Joint Health and Mobility: Protecting Vulnerable Areas
Joints are where bones meet, and they facilitate movement. In yoga, it’s important to know how to move your joints in alignment to prevent wear and tear, particularly in areas like the knees, shoulders, and wrists, which are vulnerable during practice.
- Shoulders: The shoulder joint is highly mobile but also prone to injury. Understanding how to stabilize the scapula (shoulder blades) and engage the rotator cuff muscles can protect your shoulders during dynamic poses like Plank and Chaturanga.
- Knees: The knee joint is crucial for poses like Warrior Pose and Chair Pose. It’s essential to maintain proper alignment by ensuring the knee does not extend past the toes in these poses. Having anatomical knowledge of the knee joint can help you avoid hyperextension and reduce strain on the knee ligaments.
- Wrists: Wrist pain is common in yoga, especially in weight-bearing poses. By understanding the anatomy of the wrist joint, you can modify poses to protect the wrists or use props to support the hands in poses like Downward Dog or Plank.
Our Yoga Teacher Training at Sage House Yoga focuses on how to protect and mobilize the joints during yoga practice. We ensure that our trainees understand how to modify poses to keep joints healthy, especially for those teaching or practicing frequently.
The Role of Yoga Anatomy in Common Poses
Understanding anatomy also enhances your ability to perform yoga postures correctly. Here are a few examples:
Standing Poses
- Tadasana (Mountain Pose) is the foundation for all standing poses. It teaches you proper alignment of your feet, legs, and spine. Understanding how the bones and muscles of the lower body connect can help you engage the right muscles and maintain balance.
Seated and Forward Bends
- In poses like Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Fold), the hamstrings, lower back, and hip flexors must be properly aligned. Learning the anatomy of these areas helps you avoid straining these muscles and ensures a deeper stretch.
Backbends
- In Cobra Pose (Bhujangasana) and Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana), understanding the anatomy of your spine and shoulders is essential. Proper alignment helps protect your lower back and engage your core and glutes for a safe, effective backbend.
Inversions
- In poses like Headstand or Shoulderstand, knowing the anatomy of the cervical spine and shoulders helps avoid strain on your neck. Strengthening the shoulder girdle is key to performing inversions safely.
How Yoga Anatomy Helps Prevent Injuries
Injury prevention is one of the key reasons yoga anatomy is so important. Here’s how:
- Proper Alignment: Knowing the anatomy of your body allows you to align your joints and muscles properly in each pose, reducing strain on vulnerable areas such as the knees, shoulders, and lower back.
- Mindful Practice: By understanding the limitations of your body, you can practice yoga mindfully, listening to your body’s signals to prevent overextension or injury. At Sage House Yoga, we emphasize listening to your body, especially during our Yoga Retreats and Yoga Teacher Training programs.
- Modification & Props: For those who may be dealing with injuries or limitations, understanding anatomy allows you to modify poses or use props to make poses safer and more accessible.
Yoga Anatomy for Teachers
As a yoga teacher, your understanding of anatomy is critical to providing a safe and effective practice for your students.
- Teaching Adjustments: Knowing the anatomy of each posture enables you to give precise adjustments that help students align their bodies properly.
- Creating Safe Classes: Teachers can design classes that respect the body’s natural limits. Understanding anatomy allows you to offer modifications for students of varying abilities and physical conditions.
If you’re passionate about teaching yoga, Sage House Yoga’s Teacher Training Program integrates yoga anatomy into the curriculum, ensuring that all graduates are equipped with the knowledge to teach safely and effectively.
The Mind-Body Connection through Anatomy
Understanding yoga anatomy isn’t just about physical alignment—it’s about creating a deeper connection between your mind and body. The more you know about your body, the more you can tune into its sensations, emotions, and energy.
In our Yoga Retreats in Rishikesh, participants often describe a profound sense of awareness and peace after practicing yoga with anatomical mindfulness. By connecting the mind to the body through anatomy, you cultivate a holistic approach to your practice—one that nurtures both physical and mental well-being.
Yoga Anatomy and Its Spiritual Benefits
Yoga is not just about physical fitness; it’s a spiritual practice. Learning about anatomy helps deepen the connection between the physical body and the subtle body (the energetic and spiritual aspects).
At Sage House Yoga, we teach that anatomical awareness can bring more mindfulness to your breath, your movements, and your intentions. This heightened awareness leads to a more fulfilling and spiritually enriching practice.
Conclusion: The Importance of Yoga Anatomy in Your Practice
Whether you’re a teacher or a student, learning yoga anatomy is essential to maximizing the benefits of your practice. It empowers you to align your body correctly, avoid injuries, and cultivate a deeper mind-body connection. At Sage House Yoga, we incorporate yoga anatomy into our Yoga Teacher Training programs and Yoga Retreats, ensuring that you have the knowledge and tools to enhance your yoga journey.
Are you ready to take your practice to the next level? Join us at Sage House Yoga to explore yoga anatomy in depth through our training programs and retreats. Deepen your practice, gain confidence in your movements, and discover the transformative power of yoga.






